Dental Bridges
What are Dental Tooth Bridges?
A bridge, also known as a fixed removable denture, is made to replace one or more missing teeth. Bridges can be supported in any of three ways:
- By natural teeth
- By implants
- By a combination of teeth and implants
A traditional bridge is made by creating a crown for the teeth on either side of the space and placing a false tooth or teeth between the crowns. The crowns, sometimes called caps, can be supported by natural teeth or by implants. The false tooth or teeth are attached to the crowns and fill the empty space. Unlike removable devices such as dentures, which you can take out and clean daily, bridges are cemented onto existing teeth.
If the teeth receiving the crowns are healthy and strong, they probably will not need root canal therapy. However, parts of the teeth will be removed to make space for the crowns. Traditional bridges are made either of porcelain fused to metal (PFM) or ceramics.
There are other types of bridges as well. A cantilever bridge is held in the mouth by one or more crowns on only one side of the space where a tooth is missing. A Maryland bonded bridge consists of a metal framework with “wings” on each side. The wings are bonded to the back of your existing teeth. The false teeth are also bonded to the framework. This type of bridge is also called a resin-bonded bridge or an acid-etched bridge.
Bonded bridges usually are not as expensive as traditional bridges. That’s because the adjacent teeth need less preparation and do not get crowns. However, these bridges are only as strong as the bonding material. Resin-bonded bridges tend not to stay cemented in place as well as other kinds in parts of the mouth where there is a lot of biting force.
Getting a bridge requires at least two visits, but often more. At the first visit, your dentist prepares the teeth and covers them with temporary crowns. The dentist may also make impressions of the teeth.
How Long do Bridges Last?
While bridges can last a lifetime, they do sometimes come loose, fall out or get decay around them. The most important step you can take to ensure the longevity of your bridge is to practice good oral hygiene. A bridge can lose its support if the teeth or bone holding it in place are damaged by dental disease. Keep your gums and teeth healthy by brushing with fluoride toothpaste twice a day and flossing daily. Also see your dentist and hygienist regularly for checkups and professional cleanings.
To prevent damage to your new bridge, avoid chewing hard foods, ice or other hard objects.
Bridges
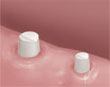 |
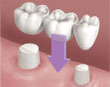 |
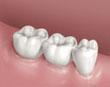 |
| Teeth around the space are prepared. | The bridge is mounted and adjusted for fit and comfort. | The bridge is cemented into position. |
